The Andean bear route in Machu Picchu captured by satellite GPS necklaces: the number of this species is increasing TLC | PERU – El diario andino







- Children’s rental cases are triggered for begging purposes: Lima concentrates most complaints
- Urgent issues in education and that were absent in the message to the nation of Dina Boluarte
Despite being an emblematic species of Peru, the Andean bear (Tremarctos ornatus) It is also one of the most vulnerable due to the various threats it faces. Therefore, in recent times, an innovative conservation strategy of this specimen based on the use of high -level technological tools is being developed, within the scope of the country’s protected natural areas (ANP) of the country.
These are necklaces with a satellite monitoring system that are placed in certain glasses of glasses (as it is also known) in order to generate fundamental information for the protection of its species. All this is possible thanks to the work articulated between the NGO Conservation of the Glash Bear (SBC) and the National Service of Natural Areas Protected by the State (Sernanp)organism assigned to the Ministry of Environment.
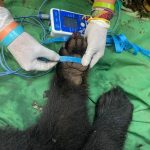
To place the necklaces, previously selected individuals are carefully immobilized. (Photo: Sernanp)
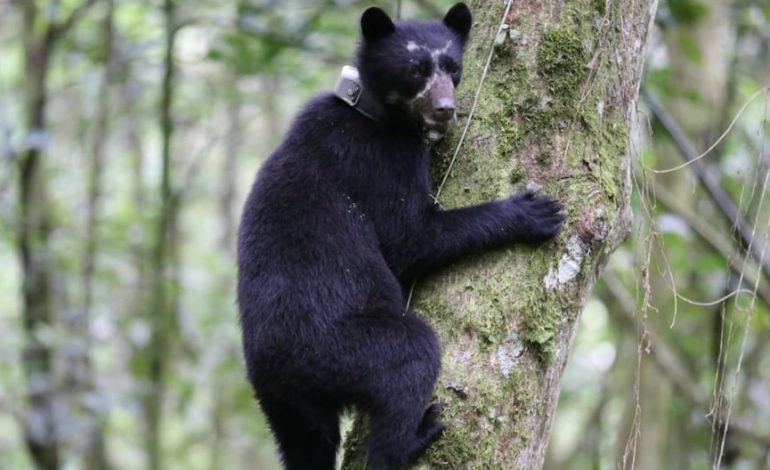
One of the sites where these devices is being used successfully is the historical sanctuary of Machupicchu, which was the first protected natural area of Peru to implement this conservation strategy. The results, to date, deserve to be highlighted.
The Andean bear route captured by satellite necklaces: the number of this species is increasing
Satellite necklaces. What are they?
Vladimir Ramírez, head of the Historic Sanctuary of Machupicchu, explained to Commerce The details of this new monitoring modality and what distinguishes it from other systems. He indicated that while monitoring to glasses of glasses It has been carried out for several decades, the new modality through satellite necklaces, which began between the end of 2022 and the beginning of 2023, helps to identify this species faster and know its behavior more precisely in order to protect it.
For this, 200 trap cameras have been installed simultaneously in the sanctuary, which helps in the visual identification of the specimens.
So far there are six Andean bears, between male and females of adulthood, who have placed the necklaces inside the Sanctuary of Machupicchu. (Photo: Sernanp)
«The collar is made up of a girdle which carries a small battery and a GPS that sends a signal to the satellite, so that in real time you can monitor the mobilization of the bears. Thus, you can know what places they feed on, which ones choose to procreate, etc. It is permanently managed to have its exact location in real time, which allows to help its conservation more effective. If they mobilize to places where they could be affected, a control and surveillance system is immediately activated”Ramírez explained.
The head of the Machupicchu sanctuary said that satellite necklaces cannot be placed to any bear. For this, a previous analysis of the most suitable specimens is carried out to take it. For example, the young are not selected, because it has to be one that can behave well with the necklace.
«The procedure contemplates carefully immobilizing individuals who are intended to choose. Six Andean bears have already been placed so far in the sanctuary, between males and females of adulthood, since each one has a different behavior. It should be noted that these necklaces are not harmful. Depending on the time of use fall alone, or in case it is required to disconnect them, this is done electronically and automatically detaches themselves“Ramírez said.
Meanwhile, Joel Mendoza, specialist of the Subdirection of Supervision, Surveillance and Control of Sernanp, commented that a methodology that can be complemented with the use of satellite necklaces is the occupation (seeing places where the species is present), which is low cost and can cover large spaces. He added that this modality is currently being developed in 7 ANP, but the idea is that it expands to a total of 9, since it is identified as an element of importance for these areas.
«Monitoring by satellite necklaces is accompanied by trap cameras, the same occupation methodology, transect monitoring, among others. We are trying to seek that other institutions are interested in the use of these necklaces so that it can be applied in other ANP and thus we can bring together the results that you throw with the data obtained from the occupation methodology. In this way we could deduce how many Andean bears there are and its distribution«He said.
Findings and the Andean bear route
Ramírez said that monitoring through satellite necklaces is already giving satisfactory results: before 2020 it was reported between 17 and 20 copies of glasses of glasses. However, from 2022 to date, 57 individuals have already been identified. «The interesting thing is that we talk only about the Sanctuary of Machupicchu, so there must be many more. But they are mostly concentrated within the sanctuary, in the 37 thousand hectares it has. They occupy 87% of the surface«He said.
Likewise, this monitoring modality has allowed identifying the places of greatest sighting of Andean bears, the routes that frequent, how they mobilize and other indicators. These animals can even mobilize to the numerous zone, that is, to places of great snow populated altitude. That is, they manage to mobilize from the bottom of the valley to the high areas (more than 6,000 m). They have great ease to mobilize in any type of geographical accident.
The collar is made up of a girdle which carries a small battery and a GPS that sends a signal to the satellite, so that in real time you can monitor the mobilization of the bears. (Photo: Sernanp)
«Some have left the sanctuary, both towards the north and south part, have also mobilized towards the regional conservation area of Choquequirao. All this allows us to make a more effective management of the species, in addition because the ecosystems where they live are in good condition, which guarantees their food and greater reproduction”, Explained the spokesman.
A clear example of the occupation of spaces and the displacement of glasses of glasses It occurs when females have to procreate, because they mobilize to other sectors, but when they are with young, they also have another modality of movement and sometimes remain longer in some places, up to two weeks. They also look for specific foods, then, they remain in a place for different foods they need to consume.
On the other hand, Ramírez explained that all the threats faced by the Andean bearsuch as forest fires, inappropriate constructions, hunting, etc. In that sense, he stressed that there are different strategies to reduce the threat that is poured into them. «For example, it is enough that they detect the smoke of a forest fire and these species tend to migrate, but happily we have practically controlled forest fires inside the sanctuary and this allows the bear to have a better comfort and/or habitat inside. Not so out of the sanctuary«, said.
Simultaneously, 200 trap cameras have been installed in the sanctuary, which helps in the visual identification of the specimens. (Photo: Michell León / SBC Peru)
For its part, Mendoza threw a fact, which although it is still necessary to investigate more thoroughly and corroborated, it can be another sample of the significant results of the use of satellite necklaces: the populations of bears that are further north (even outside the country) are a bit larger than those that are south.
“The ANP with the greatest amount of bears to date is Machu Picchu because it is where it has developed the longest time. Regarding the occupation methodology, it has shown us that in Machu Picchu, Manu and Yanachaga they are those that have a higher index. Up to 96% of the areas are occupied by glasses of glasses. When these methodologies are developed within ANP, there is also a doubt what happens to the populations that are outside ”, added.
Future look
It is projected that this research model, based on satellite necklaces, continues to develop for the next 20 years. «One of the many challenges is to respond to why there are so many individuals in such a small space, and thus many other questions, which will help the other 33 protected areas that have glasses of glassescan replicate this model”Ramírez said.
The specimens that are tracked by GPS can be subjected to veterinary blood evaluations and morphometric measurements. (Photo: Sernanp)
«I think we are on the right track and the conservation policies made by the SERNANP And the minam are successful and I think it is doing good work. This not only serves for the conservation of protected areas, but also to respond to the international commitments of protected areas«He added.
On the other hand, Mendoza explained that as a next step it continues to analyze what the activities that could be negatively impacting the bear can be. To do this, it is necessary to work with the population, that people become allies of conservation of this copy.
Before 2020 it was reported between 17 and 20 copies of glasses. However, from 2022 to date, through necklaces, 57 individuals within the sanctuary have already been identified. (Photo: Video capture)
«In that step we are and we want to continue reinforcing that issue because it is giving us results in some areas, supporting communities in some sustainable activities that do not harm the presence of bear and their habitats so much”He said.







